Know Your Triggers
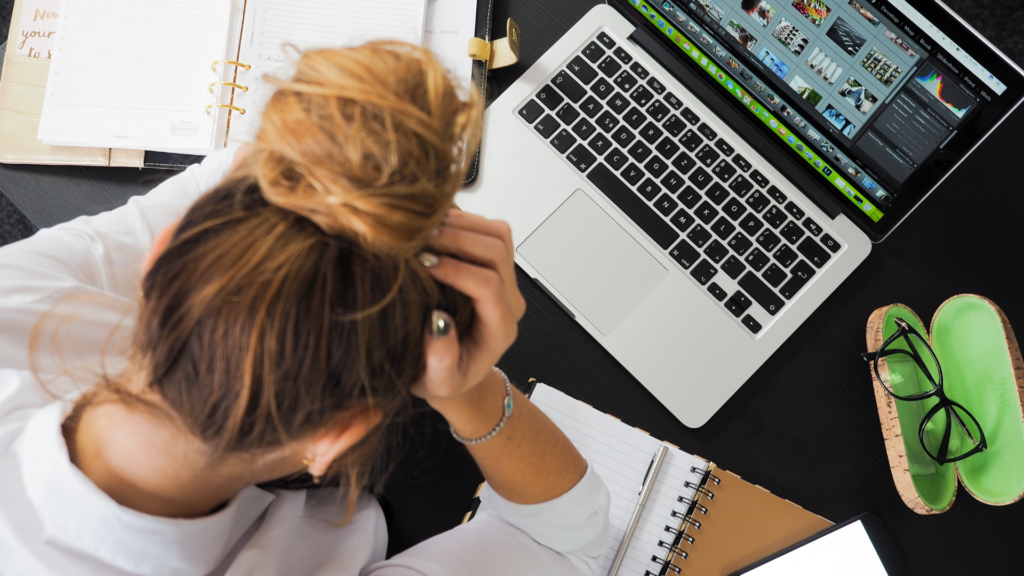
If you keep catching yourself overreacting to normal situations, feeling guilty for being “too sensitive,” and finding yourself inexplicably overwhelmed at the strangest moments, you might be triggered.
Triggers can be anything that remind you of past trauma to the point where you react like you’re in danger. The reminder might not be conscious, but your body registers the cue from the environment as a threat.
The problem is, when you don’t know you’re triggered, it’s super easy to judge yourself as being “crazy” or “too emotional.” And that kind of self-condemnation can stir up feelings of shame, which can trigger you too!
Knowing your triggers is the first step to healing. Consider some of the following types:
- Neutral triggers: These triggers aren’t safety issues, just normal aspects of everyday life. For example, let’s say you survived a terrible fire in the past. Now you’re out camping when you smell campfire smoke. Suddenly your heart starts racing, it’s hard to breathe, and fear consumes you. Logically you know there’s no real threat from the contained campfire, but your body is reacting the same way it did to the fire in the past. In this instance, it can help to remind yourself that you’re safe in the present moment.
- Dangerous triggers: It’s important to be able to differentiate harmless triggers from truly threatening ones. For example, an abusive and controlling friend might remind you of a past relationship that was also toxic. Sometimes being triggered is a sign you’re in danger and need to reach out for help.
- Upsetting but not dangerous triggers: Imagine you and your partner are stressed, a conversation gets heated, and your partner gets so upset they ask to take a break from the argument. Without warning, you’re flooded with intense feelings of worthlessness. Part of you knows your partner just needs time to cool off, but the other part is convinced they hate you and are going to leave you. In this scenario, feeling upset makes sense to some degree. Most people feel frustrated during an argument or dislike having to wait to resolve a problem. But the emotional intensity signals a deeper issue.
When you’re triggered and don’t know it, you might accidentally assume the trigger is to blame for how you feel. For instance, in the previous example, the feelings of worthlessness aren’t caused by your partner, they’re caused by past trauma. Past emotions from traumatic events can break through into the present even if the trauma occurred years ago.
When this happens, it helps to validate both your emotions that fit the situation (such as irritation with your partner), and your emotions from the past (such as fear of abandonment from a neglectful caregiver). Remind yourself that how you feel about the past is okay, it just may not apply very well to your current situation.
For more information on triggers, read “Transforming the Living Legacy of Trauma” workbook by Janina Fisher.